
In valuation and finance texts including texts by Damarodan and the McKinsey Valuation book, various methods are typically described. Depreciation is considered a tax shield because depreciation expense reduces the company’s taxable income. When a company purchased a tangible asset, they are able to depreciation the cost tax shield formula of the asset over the useful life.
Tax Shield: Definition, Formula For Calculation, And Example
Their benefits depend upon the taxpayer’s overall tax rate and cash flow for the given tax year. In addition, governments often create tax shields to encourage certain behavior or bookkeeping investment in certain industries or programs. Although tax shield can be claimed for a charitable contribution, medical expenditure, etc., it is primarily used for interest and depreciation expenses in a company.
Tax Shield formula

Real estate depreciation is a method used to deduct market value loss and the costs of buying and improving a property over its useful life from your taxes. The IRS allows you to deduct a specific amount (typically 3.636%) from your taxable income every full year you own and rent a property. Over the useful life of the machinery, the total tax shield would be $30,000 ($3,000 x 10 years). This tax shield helps to reduce the company’s tax liability, which can improve its financial performance and increase shareholder value. In these formulas, “Tax rate” refers to the applicable tax rate, which is the rate at which the taxpayer’s taxable income Accounting for Technology Companies is taxed. For example, if a company has a tax rate of 30%, the tax shield formula would use a tax rate of 0.30.

Create a free account to unlock this Template
But despite providing a handful of benefits, APV is used far less often than WACC in practice, and it is predominantly used in the academic setting. Note that since the APV is based on the present-day valuation, both the unlevered firm value and the financing effects must be discounted back to the current date. The APV approach allows us to see whether adding more debt results in a tangible increase (or decrease) in value, as well as enables us to quantify the effects of debt.
Since depreciation expense is tax-deductible, companies generally prefer to maximize depreciation expenses as quickly as they can on their tax filings. Corporations can use a variety of different depreciation methods such as double declining balance and sum-of-years-digits to lower taxes in the early years. While tax shields result in tax savings, the two concepts are not exactly the same.
- A tax shield works by reducing a company’s taxable income, which in turn reduces the amount of taxes owed.
- This can provide a tax shield by reducing the amount of taxable income subject to tax.
- However, it also considers the potential costs of financial distress that might arise from high levels of debt, as well as other financing-related impacts like subsidies or hedging.
- The 2% difference makes income of $80 and another $100 is made by the return on equity capital.
- A tax shield is the tax advantage of debt financing that arises from the deductibility of interest from the tax base and thus reduces a company’s tax burden.
- This financial benefit can free up cash that could then be reinvested in the business to further its growth and expansion.
Tax Shield Formula
Compute after-tax cost of training program if tax rate of the company is 40%. The PV of the interest tax shield can be calculated by discounting the annual tax savings at the pre-tax cost of debt, which we are assuming to be 10% in our example. However, the interest paid on these debts is tax-deductible, thus making it an attractive proposition by creating a shield against a portion of the taxable income. Hence, the Tax Shield Formula plays an instrumental role in taxation and investment planning by providing measurable benefits to individuals and corporations.
Relevance in business valuation
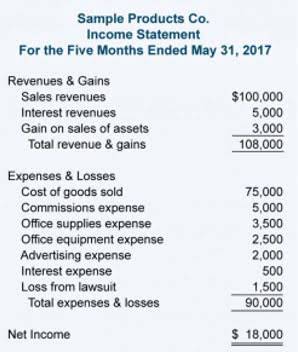
The market value of debt to the corporation is reduced to when the coupon rate falls and the equity value increases. For example if debt was 1,000 at with an interest rate of 10% and the coupon rate is reduced to 6%, the market value of debt decreases form 1,000 to 600. If the opportunity cost of debt for providers of funds is 10% both before and after the coupon rate decrease, the value of the debt declines to 60 of interest/10% or 600. Suppose the company has an interest expense of $7 million and a 25% effective tax rate. Interest expenses on certain debts can be tax-deductible, which can make the entire process of debt funding much easier and cheaper for a business. This works in the opposite way to dividend payments, which are not tax-deductible.

Does the capital structure influence the company value?
There is no tax shield formula when the IEI is available because “df” would be 100% and the full tax impact only applies to the first year. The standard present value of tax shield for CCA formula below considers the impact of the CCA deduction, including the impact of the half-year rule. This incentive was available to Canadian-Controlled Private Corporations (CCPCs) for eligible property made available for use after April 19, 2021, and before January 1, 2024. Any unused deduction limit (e.g., if the deduction is less than $1.5M for a particular year) cannot be carried forward. As for the taxes owed, we’ll multiply EBT by our 20% tax rate assumption, and net income is equal to EBT subtracted by the tax.
